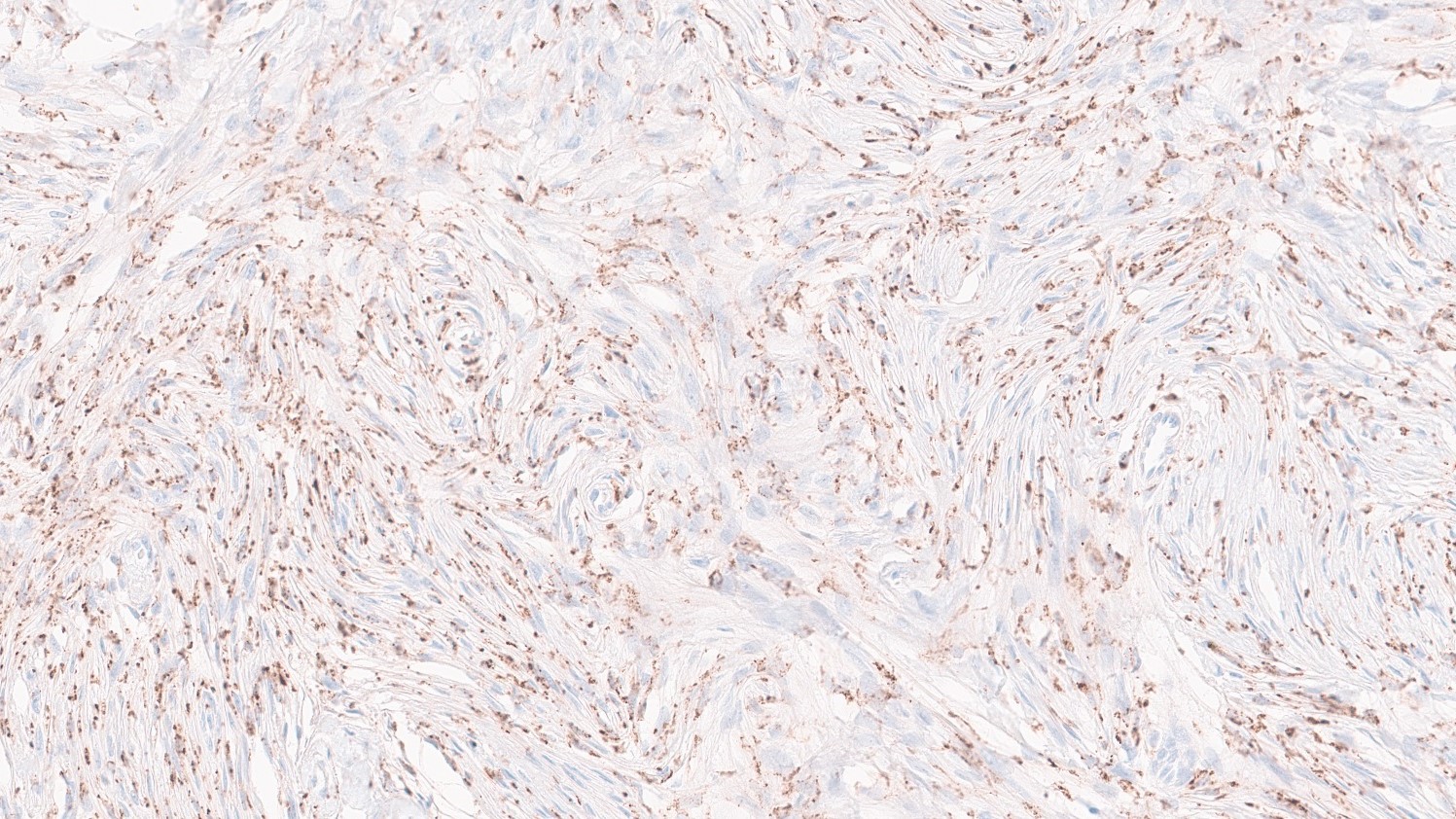
Research

Scientists at Heidelberg University’s Medical Faculty, the German Cancer Research Center, and the National Center for Tumor Diseases (NCT) in Heidelberg have shown that the molecular classification of brain tumors using artificial intelligence can be significantly influenced by the microenvironment in the tumor—in particular, the immune cells that have migrated there. Classic tissue assessment by […]
read more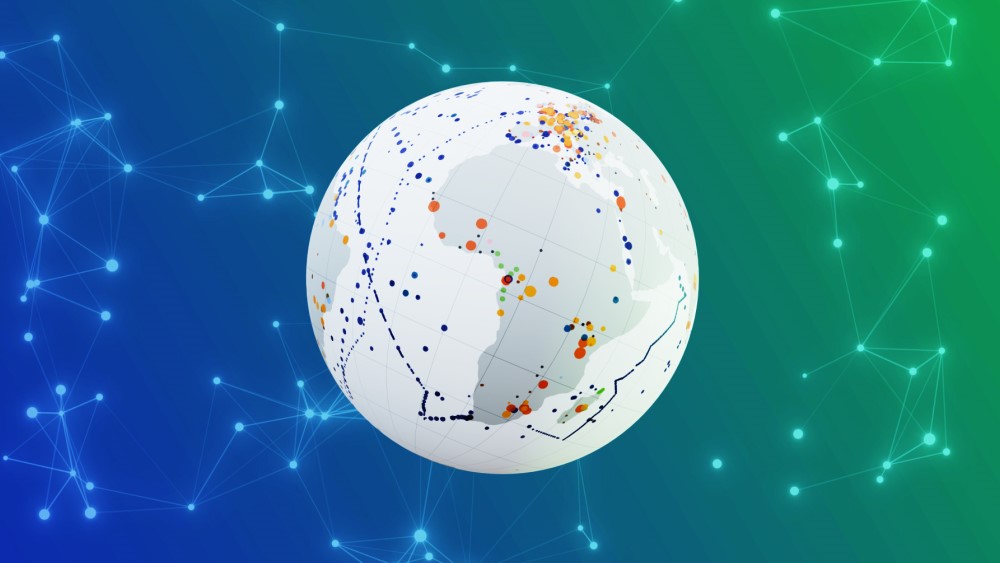
Microbiomes interconnect on a planetary-scale, new study finds
In the largest study of its kind, EMBL scientists reveal that certain microbes can thrive across different ecosystems, contributing to the global spread of antimicrobial resistance Summary In a new study published in Cell, scientists in the Bork Group at EMBL Heidelberg reveal that microbes living in similar habitats are more alike than those simply inhabiting the same geographical […]
read more
Weight Loss in Cancer: Organs Respond to the Disease in a Coordinated Way
Cachexia is a metabolic disorder that causes uncontrolled weight loss and muscle wasting in chronic diseases and cancer. A new study by Helmholtz Munich, in collaboration with the Institute of Physiology of the Czech Academy of Sciences in Prague, Heidelberg University Hospital, the German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD), and the German Center for Cardiovascular […]
read more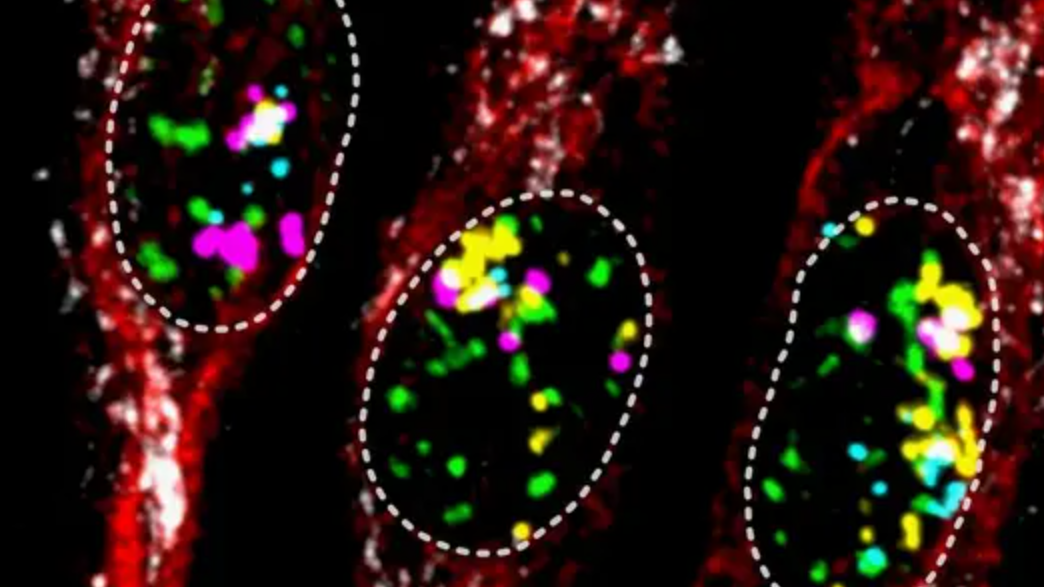
How cells control inflammatory responses
Inflammation has to work fast against pathogens—but it can’t get out of control. Researchers at the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) have now deciphered in more detail how the organism masters this balancing act. Their work shows that cells use two different strategies to precisely control inflammatory genes and thus precisely regulate the inflammatory response. […]
read more
Bayer to expand into molecular imaging with acquisition of innovative pan-amyloid radiotracers from Attralus
Bayer bolsters development portfolio by acquisition of two investigational imaging agents (AT-01 and AT-05) from Attralus, Inc. to advance diagnosis for cardiac amyloidosis / PET tracer AT-01 in Phase III and SPECT tracer AT-05 in Phase I of clinical development specifically designed for the diagnosis of cardiac as well as other types of systemic amyloidosis […]
read more
Predicting the Ever-Changing World of Protein Dynamics
In July 2025, a team of researchers from HITS and the Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research (MPIP) developed a model that learns how to generate proteins with highly flexible structures. A new, complementary deep learning model — Back Bone Flow (BBFlow) — can now predict the dynamics of proteins, providing insights into how they function. Their […]
read more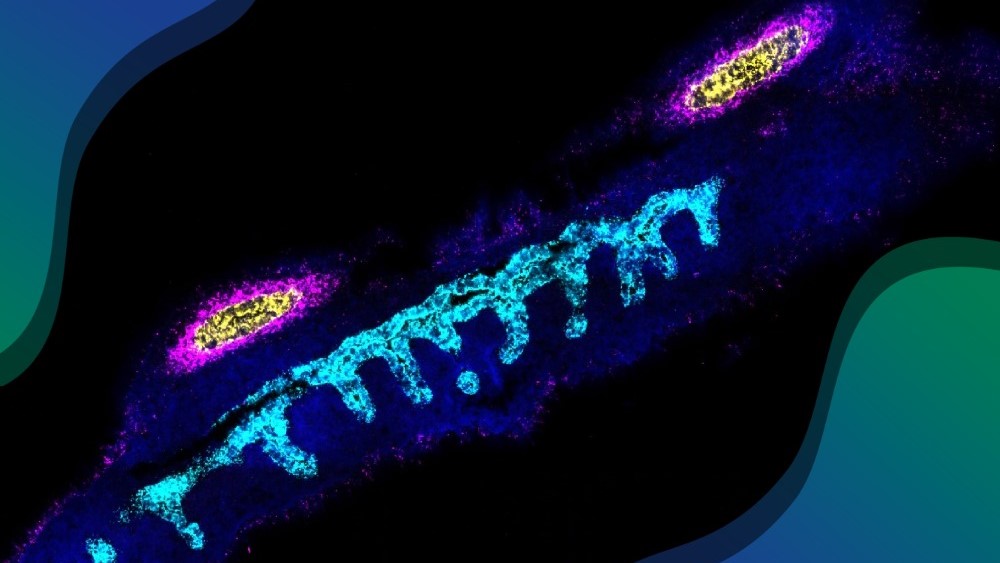
Cell map unlocks secrets of how reproductive organs form
A new single-cell map reveals how human reproductive organs form and respond to environmental influences New research has mapped the cell types that specialise to form reproductive organs in both sexes, identifying key genes and signals that drive this process. The findings offer important insights into conditions affecting the reproductive organs and how environmental chemicals […]
read more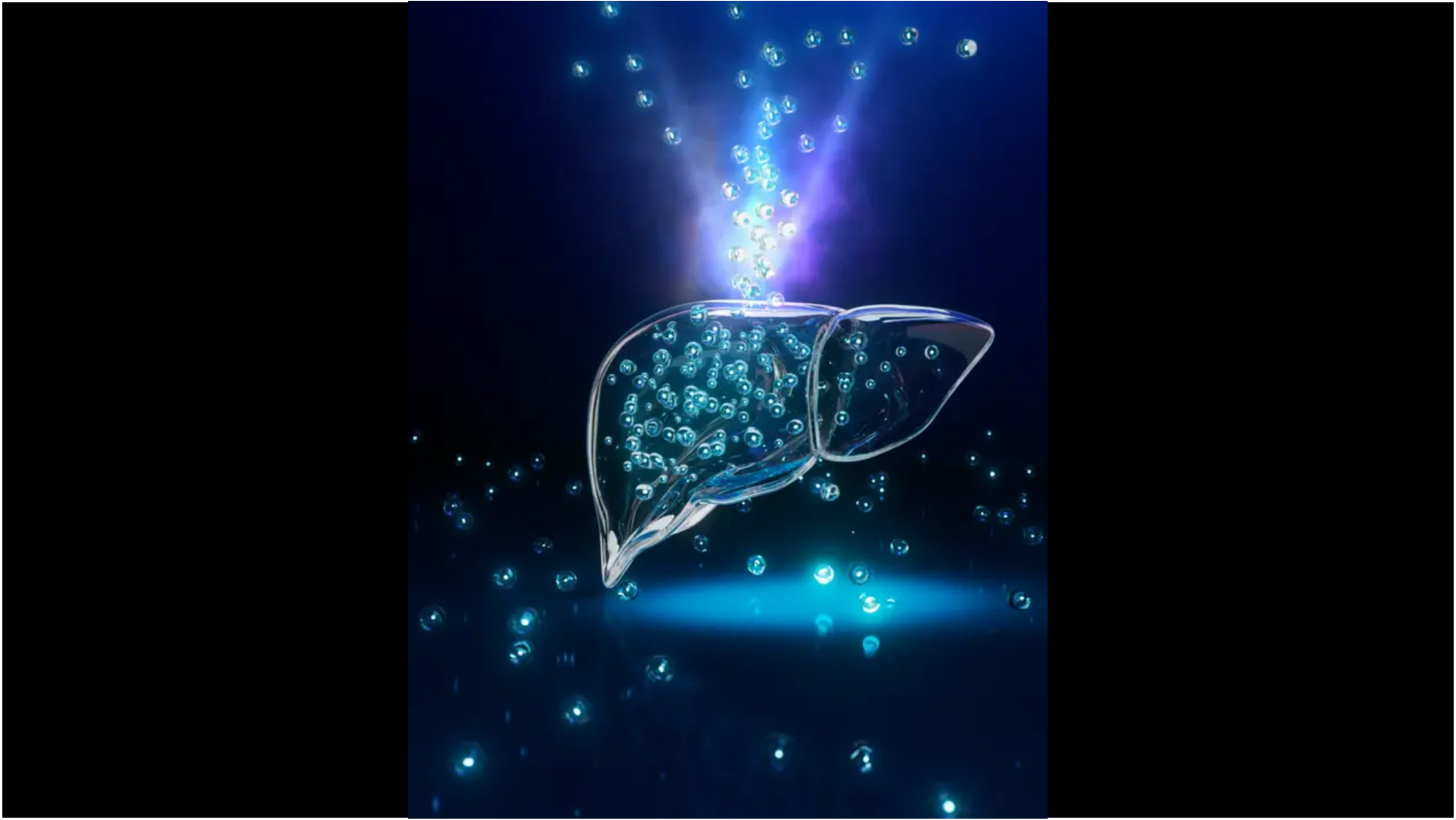
mRNA rejuvenates aging immune system – the liver as a fountain of youth
Can the weakened immune systems of older individuals be rejuvenated? Researchers from the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), HI-STEM*, and the Broad Institute have demonstrated that this is possible with an innovative approach. In a study now published in Nature, the team showed that mRNA technology can be used to transform the liver in mice […]
read more
New Publication: From Sample to Mixed Reality: A Translational 3D MALDI Imaging Platform for Advanced 3D Spatial Omics Analysis of 3D Cell Culture Disease Models
S. A. Iakab, J. Cordes, T. Enzlein, et al. “ From Sample to Mixed Reality: A Translational 3D MALDI Imaging Platform for Advanced 3D Spatial Omics Analysis of 3D Cell Culture Disease Models.” Adv. Sci. (2025): e16098. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202516098 Abstract Human 3D cell cultures, including spheroids and organoids, are essential biological models for translational pharmaceutical and biomedical research. However, their 3D analysis […]
read more
