
Research

Motion patterns help the transition between tissue compartments – explanation for asymmetry in the body plan of the pathogen With victims numbering in the millions, malaria is an infectious disease caused by the bite of a mosquito carrying the malaria parasite. After penetrating the skin, the pathogen moves with helical trajectories. It almost always turns […]
read more
Blood formation: Two systems with different competencies
It has only recently become known that two parallel systems of blood formation exist in the body, originating from different precursor cells. Researchers at the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) have developed a method to examine both systems separately in mice for the first time. Their surprising finding: the majority of immune cells do not […]
read more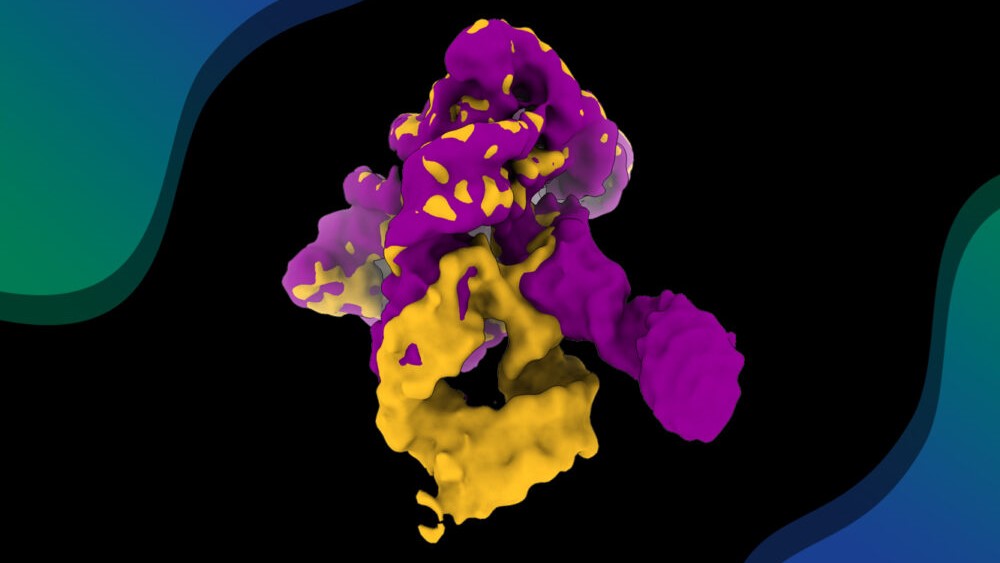
RNA in action: filming a ribozyme’s self-assembly
Researchers have visualized, in unprecedented detail, how a large RNA molecule assembles itself into a functional machine RNA is a central biological molecule, now widely harnessed in medicine and nanotechnology. Like proteins, RNA often gets its function from its three-dimensional structure. A recent study in Nature Communications has captured, for the first time, a ribozyme in motion […]
read more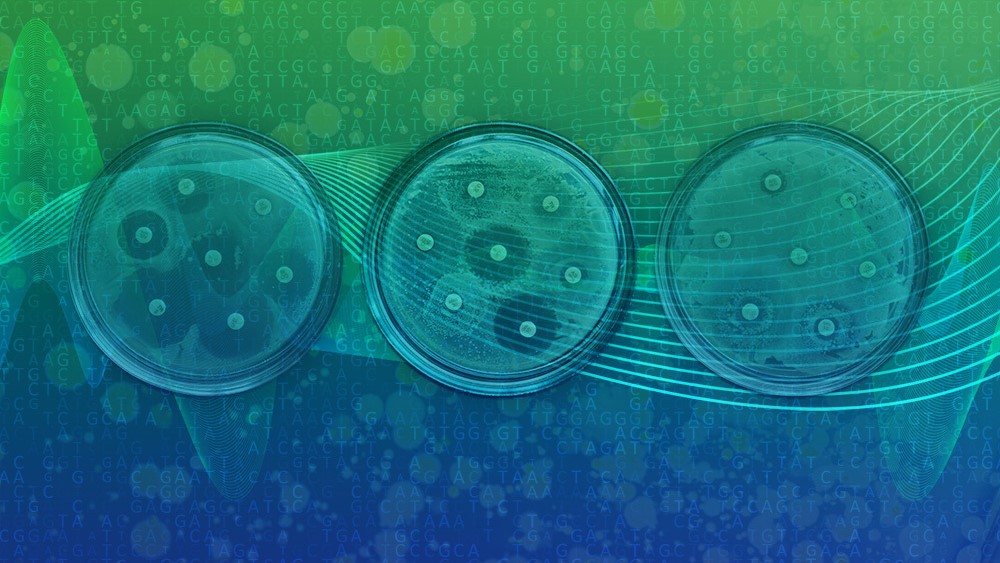
A new gateway to global antimicrobial resistance data
New online portal connects bacterial genomes with experimental resistance data to support antimicrobial resistance research Summary Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a growing health challenge, reducing the effectiveness of life-saving treatments and increasing the risk of complications from routine medical procedures. To support global AMR research, EMBL’s European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) has launched the AMR portal, a central […]
read more
New Publication: Hi-STEMProteomic Characterization Reveals CYP2S1 as a Mediator of Drug Resistance in PDACNew Publication: Hi-STEM
Abstract Objectives: To investigate the proteomic profile of different molecular subtypes of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) and understand their impact on patient outcomes, particularly focusing on pathways involved in xenobiotic metabolism and drug resistance. Methods: The study utilized the serum-free PACO cell culture model and a quantitative prefractionation-based MALDI/MS approach to establish the proteomic profiles […]
read more
How painkillers can contribute to anemia in cancer patients
Researchers from the German Cancer Research Center and the University of Freiburg show how certain painkillers influence the iron metabolism of liver cancer cells and can thus contribute to iron deficiency and anemia in cancer patients. Painkillers such as diclofenac and paracetamol are among the most commonly used drugs worldwide. They relieve pain and inflammation […]
read more
Merck and Promega collaborate on 3D cell technology for drug discovery
Full text in German below. Merck und Promega arbeiten gemeinsam an 3D-Zelltechnologie für die Wirkstoffforschung Strategische Partnerschaft bündelt Know-how von Merck im Bereich Organoide mit Promegas Assay-TechnologienForschende erhalten besseren und schnelleren Zugang zu krankheitsrelevanten ZellmodellenStärkt Mercks Position bei zukunftsweisenden Tools und Lösungen auf dem Gebiet der Biologie Darmstadt, Deutschland. (06. November 2025) Merck, ein führendes Wissenschafts- […]
read more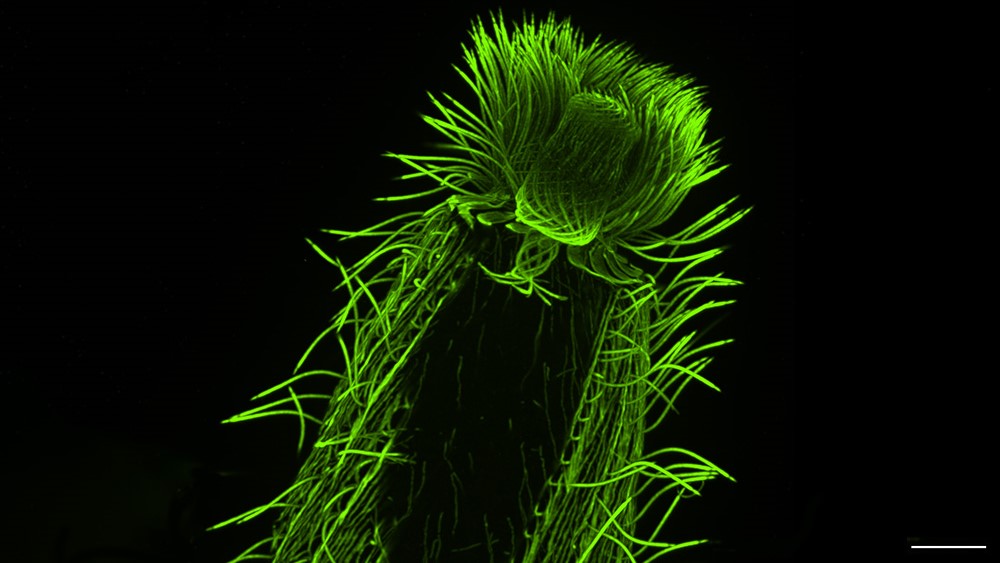
Expanding the biological world through microscopy
EMBL researchers have been using a powerful technique called expansion microscopy to peek deeper inside living organisms and understand how they function One day in 2020, in the middle of the COVID-19 pandemic, EMBL Group Leader Gautam Dey received a Zoom call from his collaborator and fellow cell biologist Omaya Dudin. Dudin, who led a research group at […]
read more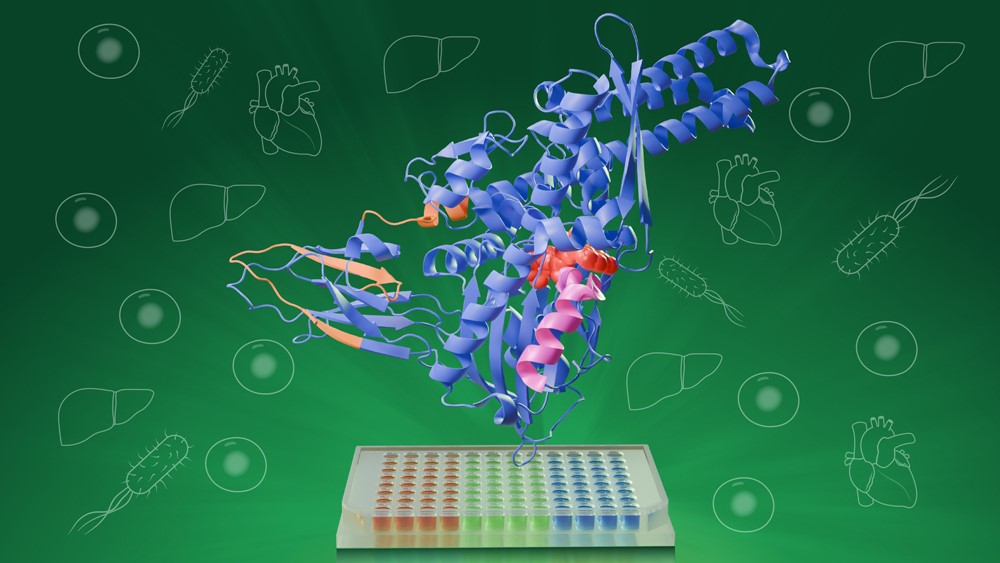
New method offers broader and faster detection of protein-ligand interactions
EMBL scientists improve a protein analysis technique, significantly expanding its use and making it 100 times faster – a development that could accelerate drug discovery and fundamental biological research Summary Swedish chemist Jöns Jacob Berzelius, in a letter to a fellow chemist, first suggested the name ‘proteins’ for a particular class of biological substances, deriving […]
read more
