New Molecular Engineering Technique Allows for Complex Organoids
Interdisciplinary research team uses DNA microbeads to control the development of cultivated tissue
A new molecular engineering technique can precisely influence the development of organoids. Microbeads made of specifically folded DNA are used to release growth factors or other signal molecules inside the tissue structures. This gives rise to considerably more complex organoids that imitate the respective tissues much better and have a more realistic cell mix than before. An interdisciplinary research team from the Cluster of Excellence “3D Matter Made to Order” with researchers based at the Centre for Organismal Studies and the Center for Molecular Biology of Heidelberg University, the university’s BioQuant Center as well as the Max Planck Institute for Medical Research in Heidelberg developed the technique.
Organoids are miniature, organ-like tissue structures derived from stem cells. They are used in basic research to gain new insights into human development or to study the development of diseases. “Until now it wasn’t possible to control the growth of such tissue structures from their interior,” states Dr Cassian Afting, a Physician Scientist at the Centre for Organismal Studies (COS). “Using the novel technique, we can now determine precisely when and where in the growing tissue key developmental signals are released,” emphasizes Tobias Walther, a biotechnologist and doctoral candidate at the Center for Molecular Biology of Heidelberg University (ZMBH) and the Max Planck Institute for Medical Research in Heidelberg.
The interdisciplinary research team of biologists, physicians, physicists, and materials scientists constructed microscopically small beads of DNA that can be “loaded” with proteins or other molecules. These microbeads are injected into the organoids and release their cargo when exposed to UV light. This allows the release of growth factors or other signal molecules at any given time and location within the developing tissue.
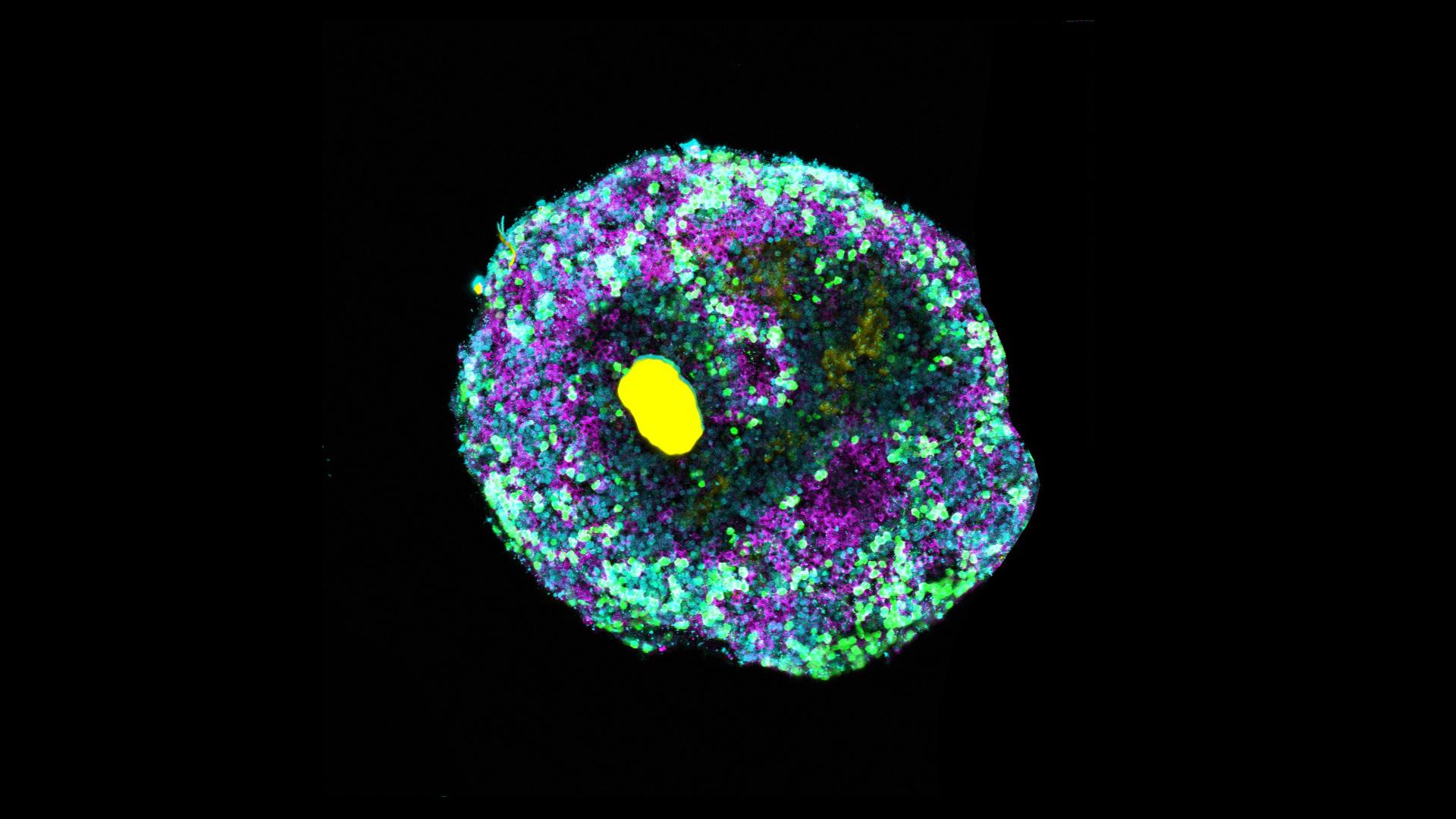
The researchers tested the process on retinal organoids of the Japanese rice fish medaka by precisely inserting microbeads loaded with a Wnt signal molecule into the tissue. For the first time, they were able to induce retinal pigment epithelial cells – the outer layer of the retina – to form adjacent to neural retinal tissue. Previously, adding Wnt to the culture media would induce pigment cells but suppress neural retina development. “Thanks to the localized release of signaling molecules, we were able to achieve a more realistic mix of cell types, thereby more closely mimicking the natural cell composition of the fish eye than with conventional cell cultures,” explains Prof. Dr Kerstin Göpfrich, a researcher in the field of synthetic biology at the ZMBH and the Max Planck Institute for Medical Research.
According to the scientists, the DNA microbeads can be flexibly adapted to transport many different signal molecules in various types of cultivated tissue. “This opens up new possibilities for engineering organoids with improved cellular complexity and organization,” states Prof. Dr Joachim Wittbrodt, who directed the research work together with Prof. Göpfrich. “More sophisticated organoid models could accelerate research on human development and disease and potentially lead to better organoid-based drug research,” states the Heidelberg developmental biologist, whose research group is located at the COS.
The new technique for creating more complex organoids was developed in the Cluster of Excellence “3D Matter Made to Order”, which is operated jointly by Heidelberg University and the Karlsruhe Institute of Technology. The research work was funded by the European Research Council (ERC) within the framework of an ERC Starting Grant for Kerstin Göpfrich, and the German Research Foundation. A paper with the research results was published in the journal “Nature Nanotechnology”.

Original publication
C. Afting, T. Walther, O. M. Drozdowski, C. Schlagheck, U. S. Schwarz, J. Wittbrodt, K. Göpfrich: DNA microbeads for spatio-temporally controlled morphogen release within organoids. Nature Nanotechnology (9 September 2024).