Therapeutic Designer Peptide to Combat Acute Heart Muscle Weakness

Researchers of the Heidelberg University, Heidelberg University Hospital (UKHD) and Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies (HITS) have developed a synthetic peptide based on the natural protein S100A1, a nearly universal “fuel” for weakened hearts. The researchers combined computer-aided methods with lab studies to investigate the therapeutic effect of the so called S100A1ct peptide molecule. The results have been published in the journal “Circulation”.
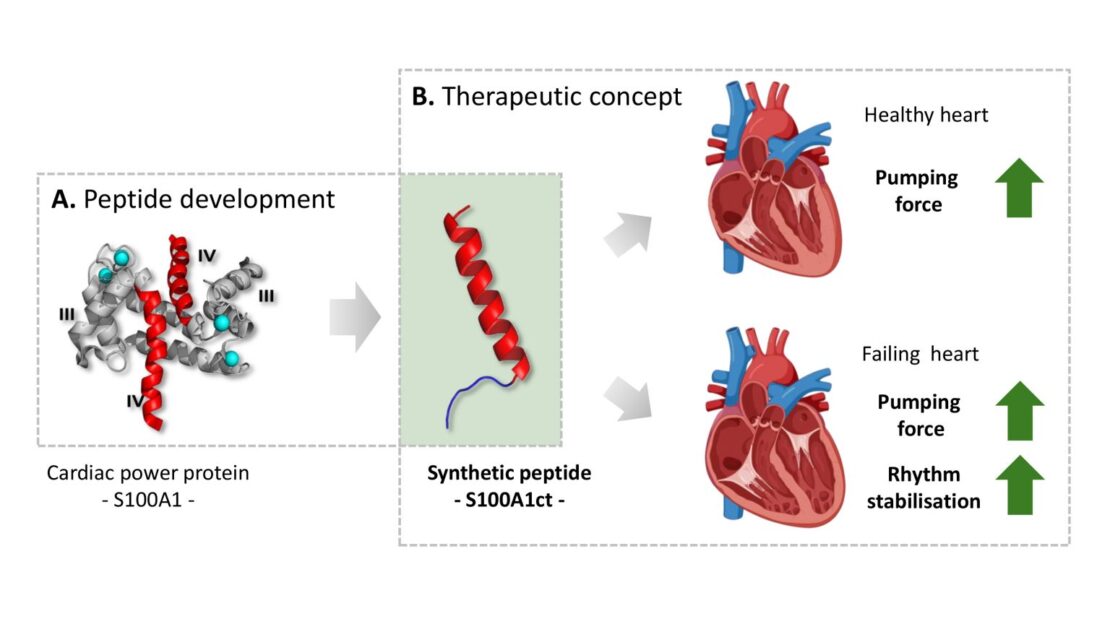
The “Molecular and Cellular Modeling” group led by Rebecca Wade was part of the project. The approach was to integrate experiments on heart muscle cells and animals and computational molecular modeling. “Our lab developed a customized computer-aided modeling pipeline for this project to model the molecular structure of the peptide and interactions with the predicted molecular effectors in the diseased heart cells”, Wade says. “The computational modeling guided the design of specific experiments to investigate the molecular mechanisms.”
The framework for the successful cooperation was provided by the Informatics for Life (I4L) Initiative, which was funded by the Klaus Tschira Foundation. The project received further financial support from the German Center for Cardiovascular Research with translational project funding from the Federal Ministry of Education and Research from the “Preclinical Confirmatory Studies” program.
For more information see the press release of the Heidelberg University Hospital:
https://www.klinikum.uni-heidelberg.de/newsroom/en/therapeutic-designer-peptide-to-combat-acute-heart-muscle-weakness/
Publication:
Kehr D, Ritterhoff J, Glaser M, et al. S100A1ct: A Synthetic Peptide Derived From S100A1 Protein Improves Cardiac Performance and Survival in Preclinical Heart Failure Models. Circulation. Published online November 21, 2024. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.123.066961
Scientific Contact:
Prof. Dr. Patrick Most
Division of Molecular and Translational Cardiology
Department of Internal Medicine III
Heidelberg University Hospital
Heidelberg Medical Faculty of Heidelberg University
patrick.most@med.uni-heidelberg.de
Prof. Dr. Rebecca Wade
Group Leader `Molecular and Cellular Modeling´
Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies (HITS)
Center of Molecular Biology of Heidelberg University (ZMBH)
Heidelberg Medical Faculty of Heidelberg University
Press Contact:
Dr. Stefanie Seltmann
Head of Communications
Heidelberg University Hospital (UKHD)
presse@med.uni-heidelberg.de
Dr. Peter Saueressig
Head of Communications
Heidelberg Institute for Theoretical Studies (HITS)
comms@h-its.org